paper
process and operation of producing high carbon ferromanganese by electric furnace method
updated: 2022-04-28 attention:
electric furnace method is a method to produce high carbon ferromanganese in a reduction electric furnace with low furnace body with electric energy as heat source and coke as reducing agent. since the amount of coke required by the electric furnace method is much less than that of the blast furnace method, and the amount of charge required for smelting a ton of high-carbon ferromanganese is also less, the phosphorus content in the products is relatively low, so it is easy to obtain low phosphorus products. in foreign countries, due to the rapid development of electric power industry, the iron and steel industry has a large demand for electric furnace high-carbon ferromanganese, and the production of high-carbon ferromanganese has gradually shifted from blast furnace to electric furnace; some areas even stopped the production of blast furnace ferromanganese and switched to electric furnace to produce high-carbon ferromanganese. in china, due to the abundant coal resources, the current power supply is still relatively tight, and the grade of manganese ore resources is relatively low, so that the production of blast furnace ferromanganese still occupies a large share. for a long time in the future, blast furnace method will still be one of the main methods to produce high carbon ferromanganese in china.
1、 smelting principle
the smelting of high carbon ferromanganese is mainly a process in which the high valence oxides of manganese are heated and decomposed into low valence oxides and further reduced into manganese metals. the high valence oxide of manganese has poor stability and is easy to decompose after heating. controlling the smelting temperature of high carbon ferromanganese not to exceed 1500 ℃ can effectively inhibit the reduction of silicon dioxide. the actual allowable silicon content of high carbon ferromanganese shall not be greater than 4%, and most of them enter the slag in the form of silicon dioxide. other oxides in the charge, such as calcium oxide, magnesium oxide and aluminum oxide, are more stable than manganese oxide. under the condition of high carbon ferromanganese smelting temperature, they cannot be reduced by carbon and almost all enter the slag. the sulfur in the charge mainly comes from coke. organic sulfur volatilizes at high temperature, and the sulfur in sulfate is generally melted in the slag in the form of manganese sulfide or calcium sulfide. usually, only about 1% of the sulfur in the charge is melted into the alloy.
2、 smelting process operation
1. main production methods
the smelting of high carbon ferromanganese in electric furnace is continuous, that is, continuous feeding smelting and regular tapping. according to the different grades of manganese ore and the different basicity control of slag, there are three methods to produce high-carbon ferromanganese in electric furnace: flux method, no flux method and less flux method: flux method. alkaline slag operation is adopted. in addition to manganese ore and coke, a certain flux (lime) is added into the furnace charge, and sufficient reducing agent is used. high alkalinity slag is used for operation, and the alkalinity of slag is controlled between 1.3-1.4, so as to minimize the manganese content in slag and improve the recovery rate of manganese. flux free method. acid slag operation is adopted, lime is not added to the charge, and smelting is carried out under the condition of insufficient reducing agent. with this method, not only high carbon ferromanganese can be obtained, but also low phosphorus and rich manganese slag containing about 30% manganese for the production of manganese silicon alloy and medium and low carbon ferromanganese can be obtained for the production of manganese silicon alloy. the advantages of flux free smelting are low power consumption and high comprehensive recovery of manganese. the disadvantage is that due to the operation of acid slag, the carbon lining is seriously eroded in the smelting process and the service life of the lining is short. low flux method. the "partial acidic slag method" between flux method and non flux method is adopted. this method is to add a small amount of lime or dolomite into the ingredients, control the basicity of the slag between 0.6-0.8, and smelt under the condition of weak carbon to produce qualified high-carbon ferromanganese and low phosphorus, iron and manganese slag containing 25-40% manganese and an appropriate amount of calcium oxide. when this slag is used to produce manganese silicon alloy, it can not only reduce the amount of lime, but also reduce the amount of dust increased by lime deliquescence, so as to improve the permeability of furnace charge. foreign electric furnace smelting of high carbon ferromanganese mostly adopts no flux method and less flux method. in view of the situation of domestic resources, flux production is the main production method in china. in recent years, with the import of foreign high-grade manganese ore, in order to make rational use of rich ore resources, the main manufacturers also use non flux method and less flux method to produce high-carbon ferromanganese.
2. smelting process operation
the operation process of high carbon ferromanganese in electric furnace mainly includes batching, feeding, furnace condition maintenance, tapping and casting, etc. proportioning and feeding: after the proportioning ratio is calculated according to the proportioning, the proportioning shall be weighed in the order of manganese ore, coke and lime (dolomite), and then the prepared materials shall be sent to the feeding platform or furnace top silo through the conveying system, which shall be added to the furnace in batches according to the needs of the furnace. small electric furnaces generally use manual charging, while large and medium-sized electric furnaces are controlled to be added into the furnace through the charging pipe under the top silo. the charging position in the furnace shall be closed and the charging pipe shall be directly controlled at any time. when the furnace charge melts and sinks, the material in the material pipe will automatically fall into the furnace. with the rapid development of science and technology and the improvement of control level, most of the newly designed large-scale electric furnace weighing and feeding systems adopt computer control technology, which makes the weighing, batching and transportation process of raw materials automatic.
furnace condition maintenance. in the process of electric furnace smelting, due to the fluctuation of raw materials, the influence of electrical and mechanical equipment and other factors, the furnace condition is difficult to maintain a stable state for a long time and is always fluctuating and changing. therefore, it is necessary to observe and monitor the furnace condition at any time, make accurate judgment according to its changes, and take measures to adjust and deal with it in time to restore the furnace condition to normal state. the monitoring means of furnace condition include: observation in the furnace. for open furnace and semi closed furnace, the situation in the furnace can be observed, such as charge level distribution, charge permeability, electrode position and its insertion depth, charge level temperature, etc. discharge observation. mainly observe the temperature and fluidity of molten iron and slag during tapping, as well as the composition analysis of products and slag. instrument monitoring. electric furnace monitoring instruments mainly include ammeter, voltmeter, active power meter, electrode position indicator, furnace gas temperature, pressure, furnace bottom thermometer, etc. for the closed electric furnace, since it is impossible to observe in the furnace, the monitoring of the above control instruments is particularly important. the above observation and monitoring is an important basis for judging the furnace condition. in order to ensure the normal operation of smelting, the furnace condition should also be controlled from the following aspects: operating voltage. the melting point and boiling point of high carbon ferromanganese are low, and it is easy to evaporate when the temperature is higher than 1500 ℃. therefore, while ensuring the service load, the operating voltage and current should be reasonably selected to make the energy distribution in the input furnace reasonable. if the operating voltage is too high, the furnace charge in the reaction zone will overheat, resulting in a large amount of volatilization of manganese; if the operating voltage is too low, the productivity will be reduced and the power consumption will be increased. for electric furnaces with different capacities, the operating voltage shall have a reasonable parameter, as follows:
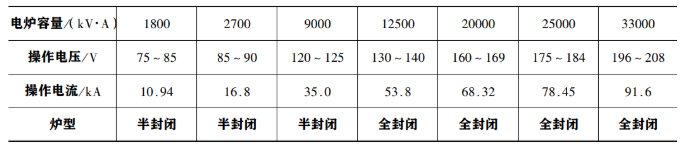
electrodes. in submerged arc furnace smelting, the working condition of electrode is an important sign to measure whether the furnace condition is normal or not. the requirements for the electrode in the smelting process are: appropriate working end length and insertion depth, and the depth of the three-phase electrode in the furnace charge shall be consistent as far as possible, so as to form a more uniform temperature field in the furnace. the depth of electrode insertion into the charge is related to the ratio of coke, slag alkalinity and operating voltage. the change of insertion depth affects the furnace condition in turn. in order to ensure the insertion depth of the electrode, the above influencing factors should be adjusted and controlled.) furnace pressure and furnace gas. for closed furnace, when the furnace condition is normal, the pressure in the furnace shall be kept at micro positive pressure, and the hydrogen content of furnace gas shall be less than 8% and the oxygen content shall be less than 3%. if the pressure of the furnace is too high, the sealing of the furnace will be damaged, and the gas will leak out, which is prone to personal safety accidents; too low furnace pressure (under negative pressure) will suck air into the furnace and increase the oxygen content in the gas, which is easy to cause explosion and even explosion accidents. the fluctuation of furnace pressure may be caused by many powder materials, high moisture, slag turnover in the furnace, cooling water leakage, flue blockage and other reasons. the causes should be found out in time for adjustment and treatment. the increase of hydrogen content in furnace gas may be caused by the increase of furnace charge moisture or water leakage of cooling system in the furnace; the increase of oxygen content indicates that the sealing system of the furnace is damaged and the air enters the furnace. in case of the above conditions, the boiler shall be shut down immediately for inspection and treatment.
the important signs of normal furnace condition judgment and treatment are: stable operating current, appropriate electrode insertion depth and normal electrode pressure and discharge speed. the height of the charge surface is appropriate, the fire is uniform, the chemical material of the furnace charge is uniform, and the phenomenon of pricking fire and material collapse around the electrode is less. the pressure, composition and temperature of furnace gas in the closed furnace are normal. the slag composition is relatively stable, the slag fluidity is good, and the slag discharge is smooth. the alloy composition is stable, the output is stable, and various technical and economic indexes are good. there are many factors affecting the stability of furnace conditions, such as the fluctuation of raw material composition, moisture and particle size, the change of electrode working end length and insertion depth, the change of slag composition and alkalinity, and the influence of mechanical and electrical accidents. however, the deterioration of furnace condition is mostly caused by too much or insufficient reductant and too high or too low basicity of slag. when there is too much reductant, due to the decrease of charge resistivity, the increase of current, the lifting of electrode, the speed of chemical material in the furnace slows down, the serious fire around the electrode, the increase of furnace gas pressure and temperature, the volatilization loss of manganese increases, the decrease of furnace bottom temperature, the difficulty of discharging, and the increase of silicon content of products. at this time, an appropriate amount of carbon reducing material shall be added around the electrode, and the amount of coke in the whole batch shall be adjusted. when the reducing agent is insufficient, the electrode is inserted too deep, and the electrode consumption increases; insufficient load and unstable current; slag turning at furnace mouth; the manganese content of slag increases, the silicon in the product is low, the phosphorus is high, the slag is more and the iron is less. at this time, an appropriate amount of coke can be added around the electrode and the coke ratio can be increased in the batch. when the basicity of slag is too high, the electrode rises in the furnace; burning and slag turning on the material surface; the slag has poor fluidity, less iron tapping, dark and rough slag, porous section and rapid pulverization after cooling. when the basicity of slag is too low, the electrode is inserted deeply, the slag is thin, the fluidity is good, the wrinkles on the slag surface are less, and more manganese runs in the slag. in view of the above situation, the dosage of lime should be adjusted in time to adjust the basicity of slag to the normal range. in addition, due to too much powder and too high moisture brought into the raw materials, it will cause poor air permeability in the furnace, serious fire pricking and material collapse, and affect the smelting technical and economic indicators. for open furnace, iron brazing can be used to pierce holes around the electrode to improve the condition in the furnace. for closed furnace, we should strictly control the quality of raw materials into the furnace to prevent the above phenomena.


 wechat
wechat