paper
process and principle of smelting high carbon ferrochromium in electric furnace
updated: 2022-04-26 attention:
smelting methods of high carbon ferrochromium include blast furnace method, electric furnace method, plasma furnace method, smelting reduction method, etc. only special pig iron containing about 30% chromium can be made in blast furnace; plasma furnace method and smelting reduction method are new processes for smelting high carbon ferrochromium, which have not been widely used. at present, high carbon ferrochromium with high chromium content is mostly smelted in submerged arc furnace by flux method.
1、 basic principle of electric furnace smelting
the basic principle of smelting high carbon ferrochromium by electric furnace method is to reduce the oxides of chromium and iron in chromium ore with carbon. the main reactions are:
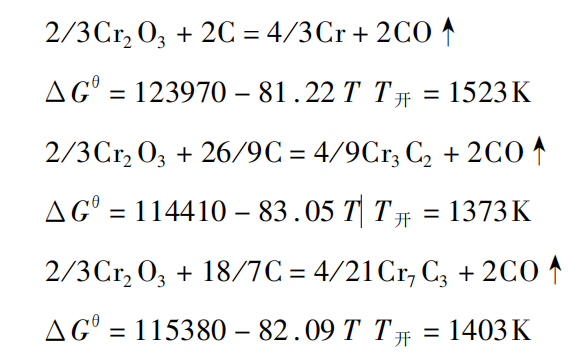
it can be seen from the above reactions that the starting temperature of carbon reduction of chromium oxide to form cr3c2 is 1373k, the starting temperature of the reaction to form cr7c3 is 1403k, and the starting temperature of the reaction to reduce chromium to form chromium is 1523k. therefore, when carbon reduction of chromium ore, chromium carbide is obtained, not metal chromium. therefore, only high carbon ferrochromium with high carbon content can be obtained. moreover, the carbon content in ferrochrome depends on the reaction temperature. it is easier to form carbides with high carbon content than carbides with low carbon content. in actual production, part of the chrome ore reacts with coke to form cr3c2 during the heating process of the charge. with the increase of the charge temperature, most of the chrome ore reacts with coke to form cr7c3, and the temperature further increases. chromium trioxide plays a role in refining and decarbonizing the alloy.
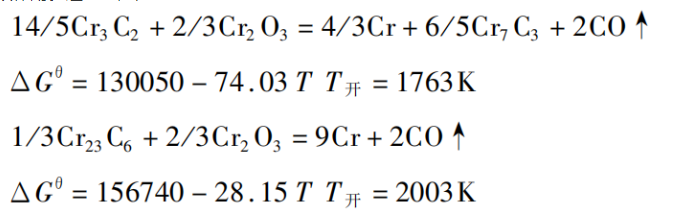
the starting temperature of iron oxide reduction reaction is lower than that of chromium trioxide reduction reaction. therefore, the iron oxide in chromium ore is fully reduced at a lower temperature and miscible with chromium carbide to form composite carbide, which reduces the melting point of the alloy. at the same time, due to the mutual dissolution of chromium and iron, the reduction reaction is easier to carry out.
2、 smelting process operation of high carbon ferrochromium
continuous operation method is adopted in the production of high carbon ferrochromium by electric furnace flux method. raw materials shall be batched in the order of coke, silica and chrome ore to facilitate uniform mixing. the open furnace adds the material around the electrode through the feed chute, and the material surface is a large cone. in the closed furnace, the material is directly added into the furnace through the blanking pipe. whether it is an open furnace or a closed furnace, new materials shall be supplemented in time with the sinking of furnace materials in the furnace, so as to maintain a certain material level. when the furnace condition is normal, the three-phase current is balanced, the electrode is stable, the air permeability is good, there is no fire, and the furnace charge can sink evenly; the temperature of slag iron is normal, the composition of alloy and slag is stable, and can be discharged smoothly from the furnace; the furnace pressure of the fully enclosed furnace is stable, the furnace gas volume and furnace gas composition change little, and there is no explosion in the feed pipe when the raw materials are dry. the number of tappings depends on the capacity of the electric furnace, and iron and slag are discharged from the taphole at the same time. in the late stage of tapping and when the slag is not smooth, the round steel shall be used to unblock the furnace hole to help discharge the slag. the plugging depth shall be determined according to the scouring degree of furnace lining. the carbon brick lining is plugged with refractory clay ball, and the magnesia brick lining is plugged with a certain proportion of magnesia powder and refractory clay ball.
the characteristics of abnormal furnace conditions are as follows: 1. when the amount of reducing agent is insufficient, the electrode is inserted deeply, the current fluctuates, the load is insufficient, and the electrode consumption is fast; the flame at the furnace mouth is dark; the alloy has low silicon and carbon content, hard iron, many skin bubbles, increased cr3c2 content in slag and increased slag viscosity. 2. when the reductant is excessive, the electrode is inserted shallowly, the current fluctuates, the electrode is burned, the slag is sprayed, and the electrode consumption is slow; the furnace bottom temperature is low, the taphole is not easy to open, and the slag is not easy to discharge; with the increase of carbon and silicon in the alloy, the content of cr3c2 in the slag decreases. 3. when there is too much silica, the electrode is inserted deeply, the flame is dark, the fluidity of the slag is good, the content of cr3c2 in the slag increases, the solidified slag blackens, the furnace wall erodes seriously, the carbon content in the alloy increases, the superheat of the alloy is small, and it is not easy to discharge from the furnace. 4. when there is too little silica, the electrode is inserted shallowly, the furnace mouth temperature is high, and there are viscous slag around the electrode, which is easy to turn over the slag. the slag has high viscosity and is not easy to be discharged from the furnace. due to the high furnace temperature, the hot metal temperature is high, the carbon content decreases, and the amount of slag iron is small. 5. when the amount of silica and coke is insufficient, the content of cr3c2 in the slag is low and viscous. it contains many unreduced chromium ore and small metal particles, which is not easy to flow out of the furnace, and the content of silicon and carbon in the alloy is reduced. 6. when the amount of coke is insufficient and the amount of silica is excessive, the slag temperature is low, fusible and viscous, containing a large amount of silica, cr3c2 and iron oxide, the silicon content in the alloy decreases and the carbon content increases; the electrode is inserted deeply, and the consumption increases. 7. when silica and coke are surplus, the slag is easy to melt, and some coke with slag is discharged from the tap hole; the content of silicon and carbon in the alloy is high; unstable insertion of electrode. 8. when there is excess coke and insufficient silica, the electrode is lifted up, there is a pricking fire, and the coke is ejected from the crucible; the melting point of slag is high, the temperature of slag is also high, the content of cr3c2 in slag is low, the slag is viscous, and it is not easy to discharge from the furnace. the content of chromium in the alloy depends on the ratio of chromium to iron in chromium ore and the recovery of chromium. the carbon content in the alloy is mainly related to the physical properties of chrome ore. when the chrome ore has good melting property and small lumpiness, the charging speed is fast, the furnace temperature is low and the carbon content of the alloy is high; on the contrary, if the ore is difficult to melt, with large lumpiness, slow melting speed and high furnace temperature, the carbon content of the alloy is low due to the refining effect of cr3c2 on chromium carbides in the lump ore. the silicon content in the alloy is mainly related to the amount of reducing agent, silicon dioxide content in slag and furnace temperature. if the amount of reducing agent is large, the furnace temperature is high, and the silicon content in the slag is relatively high, the silicon content in the alloy is also high; on the contrary, the silicon content in the alloy is low. the silicon content of the alloy fluctuates between 0.1-5% in production. about 80% of the sulfur in the alloy comes from coke. therefore, low sulfur coke must be used to reduce the sulfur content of the alloy. in the smelting process of high carbon ferrochrome, the amount of flux directly affects the composition of slag. because the composition of slag determines the melting point of slag, and the melting point of slag determines the temperature in the furnace, the selection and control of slag composition is an important problem in smelting ferrochromium. proper slag composition can make the furnace reach enough temperature to ensure the smooth progress of reduction reaction and the smooth discharge of reduction products. the melting point of high carbon ferrochromium is above 1773k. in order to ensure high reaction speed and smooth discharge of the generated alloy from the furnace and separation of slag and iron, the furnace temperature must be controlled at 1923-1973k above the melting point of ferrochromium. therefore, the melting point of slag should be controlled within this range. otherwise, if the melting point of the slag is low and the temperature in the furnace is also low, when discharging, although the slag can flow out smoothly, the molten iron cannot flow smoothly due to low superheat, there will be more slag and less iron, and in serious cases, there will be only slag and no iron; if the melting point of slag is high and the temperature in the furnace is also high, the slag cannot flow smoothly due to high melting point and insufficient superheat, but the molten iron can flow smoothly, there will be less slag and more iron, and in serious cases, there will be only iron and no slag.
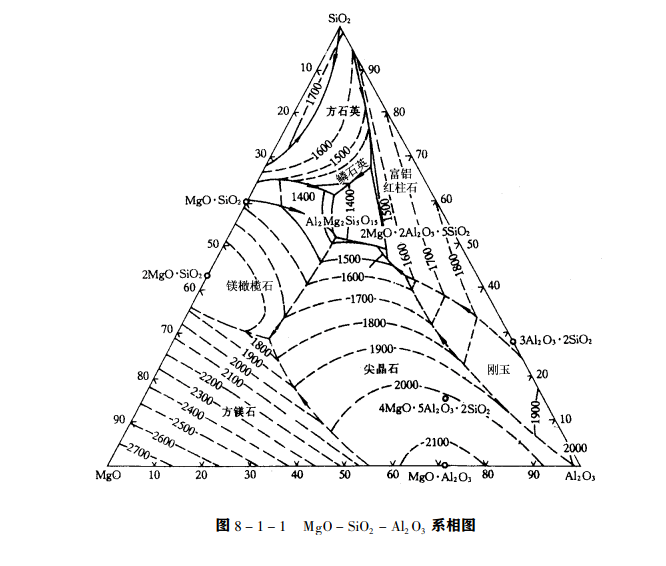
when cr3c2 and feo in chrome ore are reduced, the remaining main oxides are magnesium oxide and aluminum oxide. the melting point of both oxides must be reduced by adding silica. therefore, the amount of flux directly affects the composition of slag. the addition amount of silica is determined according to the ternary phase diagram of aluminum magnesium silicon. since the ratio of magnesium oxide to aluminum oxide in slag is about 1, a line can be drawn through the top of silica and perpendicular to the bottom. the point on the line represents the melting point of slag, which decreases with the increase of silica content. when the ratio of mgo / al2o3 changes, it has little effect on the melting point of slag, because the isoflux line is basically parallel to the bottom line. when checking the ternary phase diagram, the sum of the contents of silicon dioxide, aluminum oxide and magnesium oxide in the slag must be converted to 100%. the content of aluminum oxide in slag has an effect on the viscosity of slag. if the content of aluminum oxide in slag is too high, the viscosity of slag will increase, which is not conducive to slag discharge. however, aluminum oxide can increase the resistivity of slag and is conducive to deep insertion of electrode, so a certain content is required.


 wechat
wechat